RS-trigger. Principle of operation, functional diagrams, conversion table
Trigger is the simplest device that representsdigital automatic machine. It has two states of stability. One of these states is assigned a value of "1", and the other is set to "0". The trigger state, as well as the value of the binary information stored in it, is determined by the output signals: direct and inverse. In the case when a potential is established on the forward output, which corresponds to a logical unit, the trigger state is called single (the potential on the inverse output is zero). If there is no potential on the direct output, then the state of the trigger is called zero.

1. By the method of the recorded information (asynchronous and synchronous).
2. By the method of information management (statistical, dynamic, single-stage, multi-stage).
3. By the way of realization of logical connections (JK-flip-flop, RS-flip-flops, T-flip-flop, D-flip-flop and other types).
The main parameters of all types of triggers are the largest value of the duration of the input signal, the time delay required for switching the trigger, and also allowing the response time.
In this article, let's talk about this type of device, like the RS-trigger. They are of two types: synchronous and asynchronous.
Asynchronous RS-flip-flop constructively has two straight (R and S) inputs. This device functions according to the conversion table.
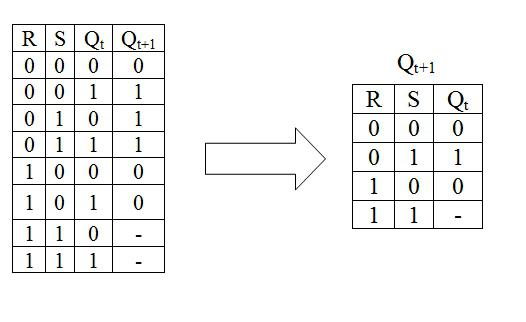
Forbidden for such a trigger isa combination of signals at the inputs of the device, causing a state of uncertainty. This combination can be expressed by the requirement RtSt = 0. When minimizing the Carnot map, the law of the trigger function is derived, which is called the characteristic equation: Q (t + 1) = St V R'tQt. In this case, RtSt will be zero.
The functional diagram shows an asynchronous type RS trigger on NAND elements and in the second execution on OR-NOR elements.

The second type is a synchronous RS-trigger. Such a device constructively has three direct inputs S, R, and C. The difference between a synchronous trigger and an asynchronous type is the presence of a synchronization input (C). It is necessary for the following reasons: after all, the inputs of the device (logic element) do not always receive signals simultaneously. This is due to the fact that they pass through different types and the number of nodes that have different delays. This phenomenon is called "competition". As a result of such "contests", the received signal values will be superimposed on the previous values of the other signals. All this leads to a false operation of the device.
This phenomenon can be eliminated by feeding to the entrancetime gating signal devices. Namely: at the input of a logic element, in addition to directly information signals, key synchronizing pulses are fed, by this time the information input signals can be fixed at the inputs.
The main condition for correct operation of the triplogical cascades in the RS-flip-flop and the logic circuits controlled by them-the inadmissibility of the simultaneous operation of the signal Rt or St switching the device, and the removal of information from the output Q (t + 1) of the flip-flop. In this regard, potential series of elements contain only synchronous ones.
The synchronous-type RS-trigger is represented by the characteristic equation: Q (t + 1) = StCt V R'tQt V QtC "t.
The photo shows a synchronous-type RS trigger on the NAND elements.