Shunting of vessels of the lower extremities: indications, consequences
Vascular diseases occur both in women and inmen. More often pathologies affect people of middle and old age. Less often vascular diseases are observed in young people. In some cases, such pathologies are congenital. Typical localization of the lesions of the vascular system are coronary, cerebral arteries, rectal and lower extremity veins. Nevertheless, with systemic vasculitis, the process can be spread throughout the body. One of the frequent reasons for contacting a surgeon is varicose veins. This pathology often occurs in women. Typical symptoms are: tortuosity of the veins, their expansion, protrusion. Another disease of the vessels is atherosclerosis. It leads to blockage of arteries and impaired blood flow. In advanced cases, both pathologies are performed by shunting the vessels of the lower extremities. It is a surgical operation, thanks to which the blood flow is completely restored.

What is the purpose of shunting the vessels of the legs?
Forced measure for diseases of veins and arteriesshunting of vessels of the lower extremities. Treatment at the initial stages is carried out conservatively. Patients suffering from atherosclerotic lesion are prescribed lipid-lowering drugs (medicines "Atorvastatin", "Fenofibrate"), diet. In varicose veins, it is recommended to wear special elastic underwear, sclerotherapy. Shunting of the vessels of the lower extremities is performed with a pronounced obstruction of the artery or vein lumen, a high risk of thrombosis and development of gangrene. This procedure is a surgical intervention, it must be performed by an angio-surgeon. Shunting is the replacement of the vessel site by the implant. As a result, the blood supply is restored, and the risk of thrombosis is significantly reduced. The shunt can be made from artificial materials or the patient's own tissues. Often an adjacent vessel of the lower extremities is used as an implant. The choice of material depends on the diameter of the damaged artery or vein, as well as on the characteristics of the pathology.
Indications for shunting of the vessels of the lower extremities
Surgery to bypass the vessels of the lowerlimbs are held in a specialized or surgical department of the hospital. It refers to complicated procedures, therefore it should be carried out only on strict indications. Vascular bypass should be resorted to if more than 50% of the diameter of the artery or vein is obturated. Before deciding on surgery, doctors prescribe conservative treatment. Surgical intervention is performed in the absence of the effect of the therapy. There are the following indications for shunting the vessels of the lower extremities:
- Obliterating arteriosclerosis of the arteries.
- Pronounced pathology of the venous system. More often, with varicose veins and threats of thrombophlebitis, stenting or angioplasty is performed. With contraindications to such methods of treatment, a shunting of the vessels is performed.
- Endarteritis. With this pathology, the inflammatory reaction is combined with the progressive obliteration of small vessels. Gradually, the arteries are completely clogged, leading to gangrene of the foot. This disease is more common among the male population.
- Aneurysm of the arteries of the lower extremities. Pathology is dangerous high risk of bleeding, which is extremely difficult to stop.
In some cases, shunting is performedvessels of the lower extremities with gangrene of the toes or feet. The prognosis for this surgical intervention is not always favorable and depends on the area of necrosis and the individual characteristics of the organism. In some cases, the operation leads to the healing of gangrene or a decrease in the size of the affected focus.

In what situations is bypass surgery contraindicated?
Despite the effectiveness of shunting vessels,it is worth remembering that such an operation is very serious. Therefore, it is performed only in cases when other methods of treatment do not help. There are a number of contraindications to shunting. Among them:
- Hypertensive disease, not controlled by antihypertensive drugs. In this case, vascular surgery can lead to cardiogenic shock, myocardial infarction or stroke.
- Decompensated heart failure, accompanied by edematous syndrome and constant shortness of breath.
- Unstable angina.
- Acute heart failure and myocardial infarction.
- Aneurysm of the aorta, vessels of the brain.
- Paroxysmal heart rhythm disturbances.
Shunting of the vessels of the lower extremities can notto carry out with infectious diseases, skin lesions, decompensation of diabetes mellitus. In these cases, the operation is performed after stabilization of the patient's condition.
Methods of shunting
Most often, the arteries are bypassed. This is due to the fact that similar pathologies are more common. In addition, with the defeat of the veins, other methods of treatment are recommended. Among them - balloon angioplasty and stenting. As a shunt for the restoration of arterial blood flow, use a subcutaneous vein of the thigh. When a large area of damage or unsatisfactory state of the vessels used synthetic implants. There are several methods of conducting the operation. Among them:
- Aorto-bifemoral shunting. Surgical intervention is performed at the inguinal level. The essence of the operation is to create a bypass anastomosis between the abdominal part of the aorta and the femoral arteries.
- Thigh-hamstrings bypass. An anastomosis is formed between two large arteries of the lower limb. The shunt originates at the base of the thigh and is brought to the region of the knee joint (below or above the articulation).
- Crossover bypass. The anastomosis passes between the two femoral arteries (from the right leg to the left lower limb, or vice versa).
- Femotothyroid shunting. The vascular graft connects the femoral and tibial artery.
Preparing the patient for a vascular bypass operation
Preparation for shunting includesa number of diagnostic procedures, as well as the use of medications. Before the operation it is necessary to undergo a laboratory examination: OAK, OAM, biochemical blood test, coagulogram. Dopplerography of the vessels of the lower extremities, ECG, and Echocardi is also performed. To avoid thrombosis during surgery, a week before her appoint medications for liquefaction of blood. These include medicines "Aspirin cardio", "Magnikor". Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are also prescribed. In the evening, on the eve of the operation, you must stop taking water and food.
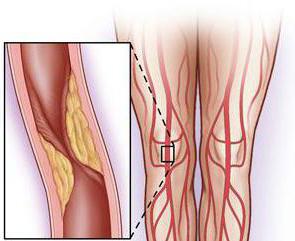
Technique of shunting the vessels of the lower extremities
Shunting of the vessels of the lower limbs isA complicated operation, for which a high professionalism of the surgeon is required. Manipulation is performed under general anesthesia. The incision of the skin and underlying tissues is performed in 2 places - above and below the affected area of the artery. The vessel is clamped to prevent bleeding. After evaluation of the affected area, an incision is made on the vessel and a shunt is fixed on one side. Then the vascular flap is fixed between the muscles and tendons. Thus, the shunt is gradually brought to the place of the second incision (above the lesion) and fixes its end. After this, the surgeon assesses the blood flow. When a successful operation artery begins to pulsate. In some cases, instrumental methods of examination are performed. The final stage of surgical intervention is the suturing of deep tissues and skin.

How is the postoperative period?
Very important is inpatient monitoring of the patient,transferred operation. Especially if this manipulation is shunting the vessels of the lower extremities. Postoperative period with successful treatment is about 2 weeks. On the 7-10th day the surgeon removes the stitches. While the patient is in the hospital, it is necessary to perform diagnostic procedures to assess the effectiveness of treatment. In addition, the doctor must be convinced of the absence of postoperative complications. Already in the first days after the operation it is recommended to get up on your feet. In the sitting and lying position, the lower limbs must be fixed in a raised state.
Recommendations in the recovery period
After shunting the vessels of the lower extremities, it is necessary to monitor the blood flow. For this purpose, the patient should undergo periodic examination (ultrasound and dopplerography). It is also recommended:
- Refuse to smoke.
- Take antiplatelet drugs to prevent thrombosis.
- Keep track of the body weight. With an increase in BMI appoint a lipid-lowering diet and medication.
- Make daily walks on foot.
- Wear special stockings (socks) and shoes.
Shunting of lower extremity vessels: patient feedback

Reviews of patients who underwent operativeinterference, mostly positive. Patients report a decrease in pain syndrome, numbness in the legs. Nevertheless, in a number of cases, people complain of the resumption of symptoms after a while. This is due to the defeat of neighboring arteries and veins. It is worth remembering that shunting is not a treatment for atherosclerosis, and the cause of the vascular lesion does not disappear after the operation. Therefore, in order to avoid thrombosis and development of gangrene, it is important to follow preventive measures.
Shunting of lower extremity vessels: complications of surgery
Complications of surgery include thrombus formationin the shunt, the development of acute heart failure, embolism of the pulmonary artery. In the recovery period, it is possible to suppuration of the wound in the area of the sutures and bleeding from it. Despite the fact that the operation is considered difficult and long (up to 3 hours), complications are rare. The frequency of their development is about 2%.
</ p>>