Baker's cyst of the popliteal fossa - treatment
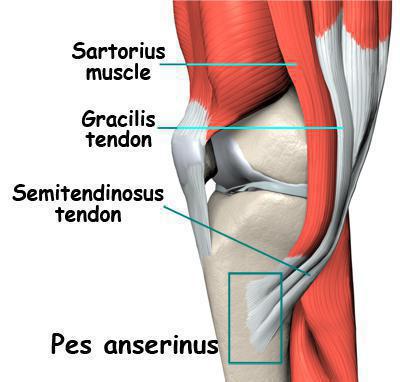
Cyst Baker popliteal fossa isa benign tumor that develops from the back of the knee joint, at the site of the popliteal fossa. It looks like a soft elastic seal, which as a result of the inflammatory process increases in size.
The place of formation is the mucosa of interstitial bags, into which liquid from the inflamed joint enters and accumulates through a narrow slit-like passage. Quite often the cyst is bilateral.
Causes: The Baker's cyst of the popliteal fossa can developindependently or against the background of damage and deformation of meniscus, chronic synovitis, osteoarthritis, osteoarthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, joint trauma, articular cartilage damage.
Symptoms: At the outset, the disease progresses unnoticedor may cause minor discomfort. At palpation, the compaction appears only when the knee is unbent, it decreases or disappears when bending.
As you grow, the pinchlocated next to the nerves, which causes tingling and numbness in the region of the feet, pain in the popliteal fossa, restriction in movements, swelling in the knee joint region. Often, it can be difficult to flex or flex the fingers.
Complications: The most common complication of the diseaseis a ruptured cyst. Occurs as a result of increased education, which provokes an increase in the pressure of the accumulated liquid. In this case, the liquid penetrates into the shin, contributing to the appearance of swelling and pain, redness and accompanied by a local increase in temperature.
The cyst of the popliteal fossa can exert pressureon the tibial nerve, causing numbness, weakness, or tingling in the lower limb. Reaching a considerable size, the cyst can press on the lymphatic, nervous and blood vessels in the area under the knee, which is caused by swelling and pain of the shin. The formation of a cyst contributes to the development of varicose tibia.
The Baker's cyst of the popliteal fossa can servethe cause of thrombophlebitis and thrombosis of the deep veins of the limb. Complication of thrombosis may be pulmonary embolism, which occurs as a result of the separation of the thrombus from the venous walls and its further movement through the body.
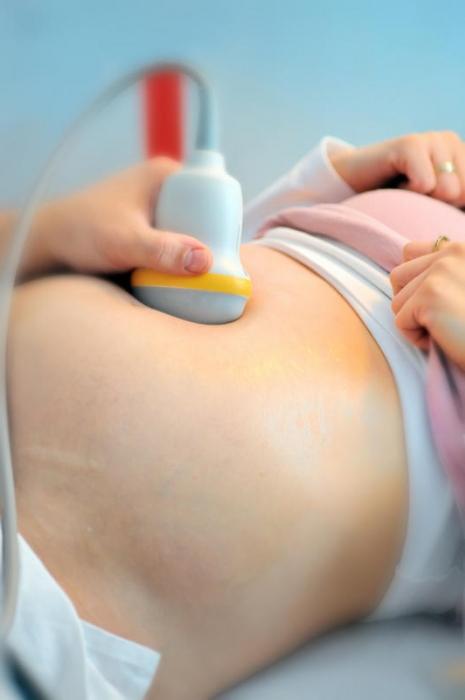
Diagnostics: Primary diagnosis of the disease is carried out onthe basis of typical manifestations of the disease. For an accurate diagnosis, the patient is prescribed ultrasound examination of the knee joint, arthroscopy (examination of the joint cavity with an arthroscope), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging tomography).
Treatment: Popper's Baker's cysts can be treated as symptomatic, andradical methods. With conservative treatment, the patient is prescribed a course of therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs, compresses, physiotherapy, intra-articular injections (drug blockades).
If the tumor grows and causes pain,a puncture is performed. The cyst is opened, the accumulated fluid is pumped out from there with the help of a thick needle. Further, the cavity is washed and anti-inflammatory steroid preparations are administered there. The conservative method of treatment does not always give a positive result.
When the tumor reaches a huge size, and alsowith significant limitations of movements and strong compression of the nerve vessels of the popliteal fossa, treatment is prescribed with the help of surgical intervention.
Operative treatment is performed through surgery,on which the cyst is excised. The surgery for excision is not very difficult, done under local anesthesia, lasts about a quarter of an hour. After the operation to remove the cyst, a tight bandage or gypsum is applied to the site of the autopsy. After 5 - 7 days the patient is allowed to walk fully.
</ p>>